Visual testing (VT)
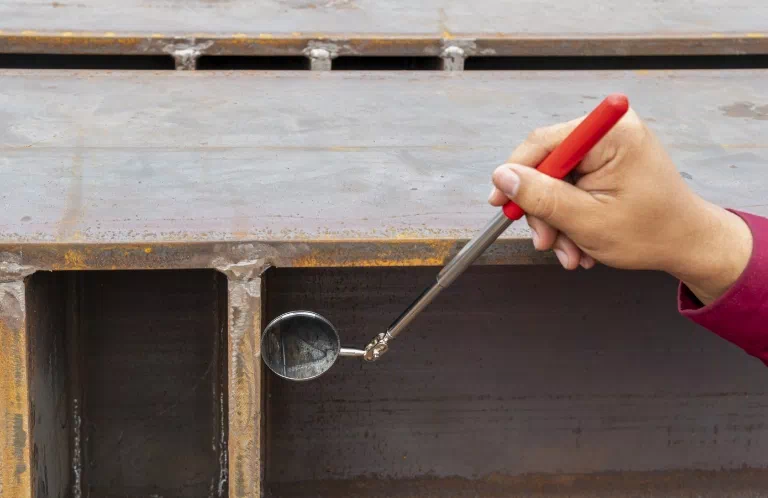

Visual testing (VT)
Visual inspections are performed by carefully observing the surface and taking preliminary measurements. This method can detect any irregularities, such as undercuts, concavity, corrosion defects or porosity. By performing this test, it is possible to check whether the joints were made in accordance with the design and whether they meet all the quality requirements.
Visual testing is divided into:
- indirect visual tests,
- direct visual tests.
For direct examinations, the naked eye is used, while for indirect examinations, elements such as an endoscope or set of mirrors are used.
Visual testing (VT)
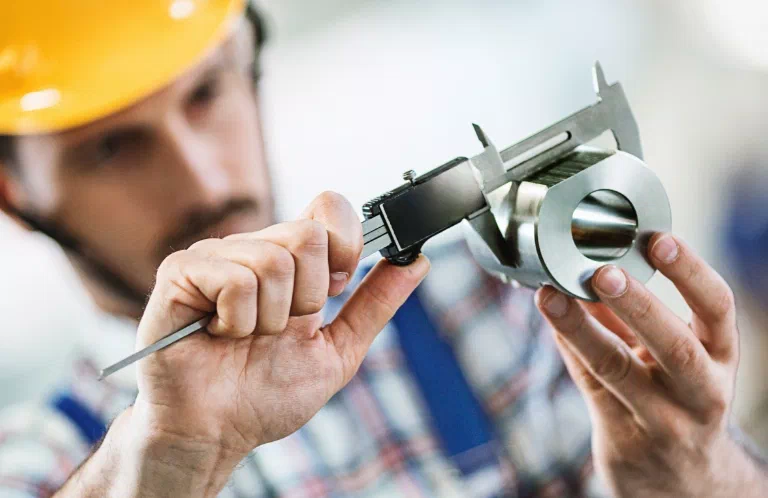

Visual inspections (VT) are used to monitor almost all manufactured products. The inspection includes, among others, castings, sheets, forgings, and welded joints. During this process, the correctness of components prepared for welding and the accuracy of their assembly are checked. Visual inspections (VT) are relatively inexpensive, highly effective, and fast. This type of inspection can be carried out at the production stage.
Visual inspections are performed at the very beginning, before, for instance, ultrasonic, penetrant, or radiographic tests.
If you are interested in commissioning VT visual inspections, please feel free to contact us!
What Are Visual Inspections?
During visual inspections, the inspector focuses on carefully examining the surface of an object, identifying any potential defects or other visible irregularities. Recognizing characteristic signs of damage, color changes, deformations, or traces of corrosion is a key aspect of this method.
Additionally, the inspected objects are compared with established quality standards to determine whether they meet specific requirements. The results of visual inspections can be documented through photographs, notes, or reports, facilitating further analysis and decision-making. In the context of structural integrity, visual inspections allow for the assessment of welds, joints, and assembly conditions.
Difference Between Indirect and Direct Visual Inspections
The difference between indirect and direct visual inspections primarily concerns the way the inspector or operator accesses the area to be examined. Here is an explanation of both terms:
- Direct Visual Inspection – This type of inspection involves the inspector or operator having direct contact with the examined area or object. It may include observing the surface, touching, manual measurements, and even using tools for a more detailed inspection. For example, an inspector may manually assess the quality of a weld by checking its smoothness, shape, or the absence of defects.
- Indirect Visual Inspection – In this case, the inspector or operator does not have direct access to the examined area. They may use tools such as reflective mirrors, video cameras, endoscopes, or other devices to inspect hard-to-reach areas. For instance, the internal parts of pipelines or equipment can be examined using an endoscope inserted inside.